AI as UI: The Shift to Conversational Interfaces
User interfaces have evolved significantly since the early days of computing, transitioning from complex command lines to intuitive graphical interfaces. With the growth of AI, there’s another major shift happening now: many services are moving from graphical user interfaces (GUIs) to conversational user interfaces (CUIs). We’re entering the era of “AI as UI.”
First Some Background: The Evolution of User Interfaces
The first computers had command-line interfaces that required users to input text-based commands. The introduction of graphical user interfaces, or GUIs, brought visual elements and icons, making computing more accessible to a broader audience. The advent of touchscreens further enhanced interactivity, allowing for more intuitive gestures for phones and tablets. Each progression aimed to make our interaction with technology more seamless and efficient.
The Rise of Conversational AI
With the growth of ChatGPT, Gemini, Co-Pilot, and many other AI-powered Chatbots, Conversational AI is rapidly becoming a commonly-used interface, but the trend can be traced much further back to the launch of assistants In  2011, Apple introduced Siri, a voice-activated personal assistant that allowed users to perform tasks through natural language commands. This was a significant milestone that brought conversational interfaces into mainstream consumer technology.
2011, Apple introduced Siri, a voice-activated personal assistant that allowed users to perform tasks through natural language commands. This was a significant milestone that brought conversational interfaces into mainstream consumer technology.
Following this, Amazon Alexa was launched in 2014, embedded within the Amazon Echo smart speaker. Alexa expanded the capabilities of voice assistants by integrating with various services and smart home devices, enabling users to control their environments through voice commands. 
Google entered the space with voice-activated services like Google Assistant. These platforms leveraged Google’s extensive data and machine learning capabilities to provide personalized assistance and information retrieval through conversational interactions.
These developments have played a crucial role in familiarizing the public with conversational interfaces. They demonstrated the practicality and convenience of interacting with technology using natural language, setting the stage for broader adoption across various applications.
Advances in natural language processing and machine learning have continued to enhance the capabilities of these assistants, making them more accurate and context-aware. From setting reminders and controlling smart devices to retrieving information and making purchases, conversational AI is becoming an integral part of the user interface landscape.
Why Conversational UI is the Future
Conversational UIs offer several advantages that position them as the future of user interaction. They provide a natural mode of communication, leveraging the inherent human ability to speak and understand language. This makes technology more accessible to individuals who may find traditional interfaces challenging, such as the elderly or those with disabilities. Additionally, conversational interfaces can enhance efficiency by allowing users to accomplish tasks through simple verbal or textual commands, reducing the need for navigating complex menus.
Applications Best Served by Conversational Interfaces
While conversational interfaces are broadly applicable, certain domains benefit significantly from this paradigm shift—sometimes in surprising ways.
Programming and Development: Traditionally, coding requires knowledge of programming languages and syntax. Conversational AI is changing this by allowing developers to describe the functionality they need in natural language, which the AI then translates into code. This accelerates the development process and lowers the barrier to entry for those new to programming. Want to see for yourself? Take a look at services like Cursor and Replit.
Content Creation and Personalization: Conversational AI is revolutionizing how we create and personalize content across various media. Users can now generate blog posts, newsletters, produce videos, and design images through simple conversational prompts. AI-powered tools interpret natural language descriptions to produce the desired content, streamlining the creative process.
Customer Service and Support: AI-powered chatbots handle routine inquiries efficiently, providing instant support and freeing up human agents to tackle more complex issues. This enhances customer satisfaction and optimizes resource allocation.
Education and Training: AI tutors interact with students conversationally, personalizing learning experiences based on individual needs and pacing. This moves beyond the traditional one-size-fits-all educational model, catering to diverse learning styles.
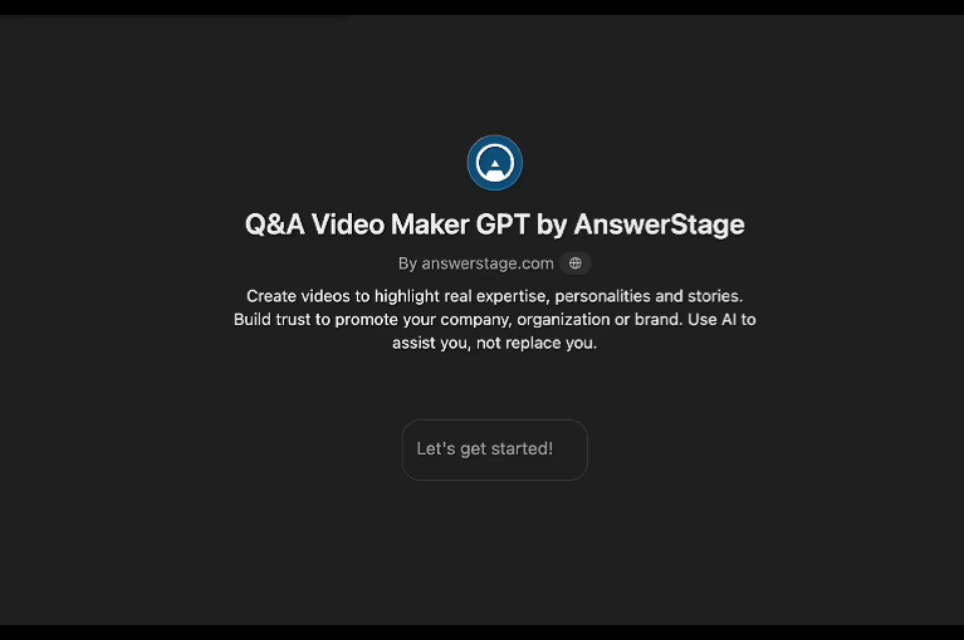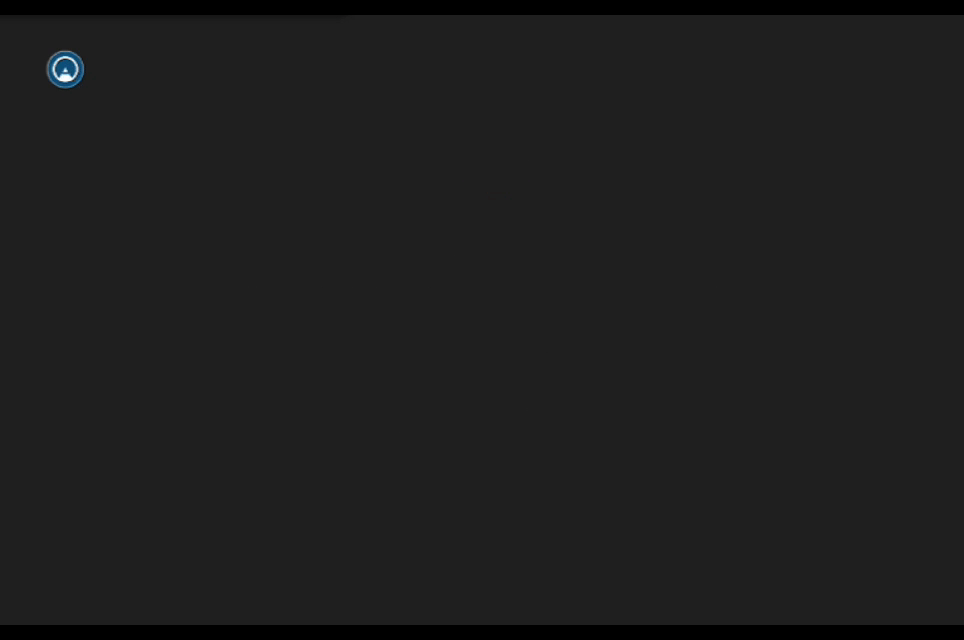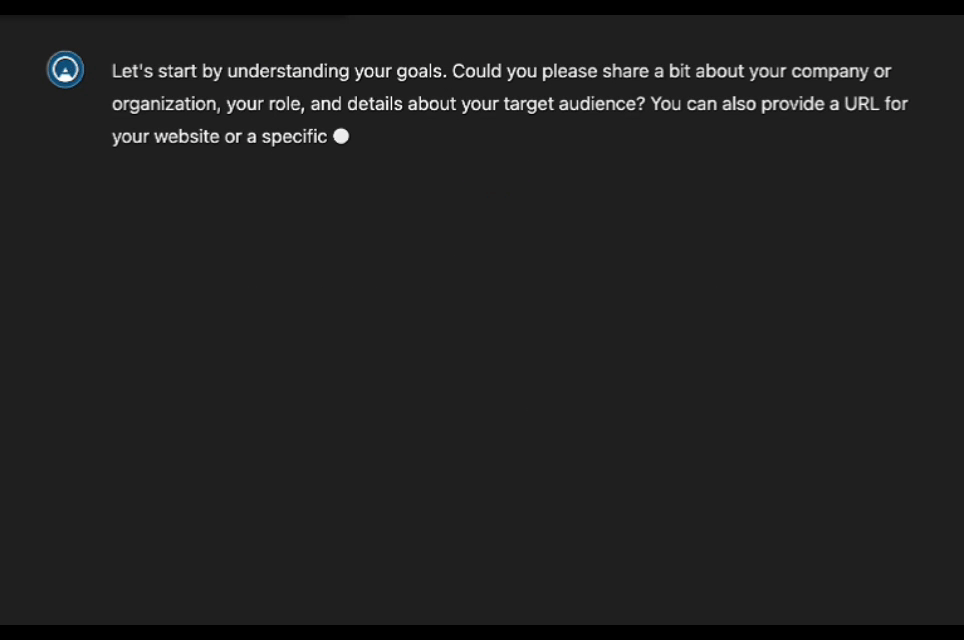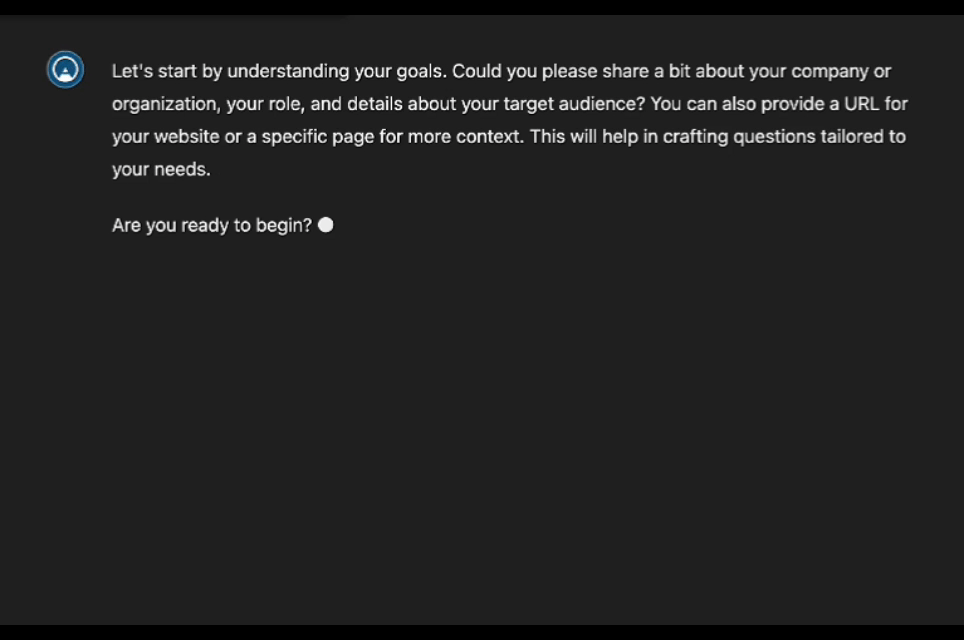
AnswerStage: Conversations Transformed Info Videos
The trend towards Conversational Interfaces is well-suited for AnswerStage. By engaging users in a Q&A format, AnswerStage leverages AI to understand the user’s role and the questions their target audience is asking. It then provides recommended talking points and scripts, which can be used with a teleprompter while recording responses. This approach not only streamlines content creation but also ensures that the messaging is aligned with audience needs. It eliminates the most common impediment to recording a video – what we refer to as “blank slate syndrome.” It’s much easier to record your thoughts when prompted with questions and provided with an outline of talking points.
Challenges and Limitations
While we’re rapidly moving towards Conversational Interfaces, several challenges need to be addressed. Privacy concerns are paramount; users need assurance that their interactions remain confidential and secure. Additionally, while AI has made significant strides, it is not infallible. Misinterpretations, hallucinations and errors can occur, leading to user frustration.
 Another significant consideration is the suitability of voice-based conversational interfaces in public or shared environments. Speaking commands or queries aloud is often impractical or uncomfortable when others are present, similar to having a phone conversation in a crowded airport terminal. This not only poses a privacy risk—since sensitive information might be overheard—but can also be socially disruptive. Users may hesitate to use voice commands in open offices, public transportation, or any setting where privacy is a concern.
Another significant consideration is the suitability of voice-based conversational interfaces in public or shared environments. Speaking commands or queries aloud is often impractical or uncomfortable when others are present, similar to having a phone conversation in a crowded airport terminal. This not only poses a privacy risk—since sensitive information might be overheard—but can also be socially disruptive. Users may hesitate to use voice commands in open offices, public transportation, or any setting where privacy is a concern.
There is also an adjustment period for users who may be unfamiliar or uncomfortable with conversational interfaces. Overcoming these obstacles is essential for the widespread adoption of AI as the primary user interface.
AI as UI – Conversational Interfaces are the Future
Conversational AI represents a significant advancement toward more human-centric technology interactions. “AI as UI” is about enhancing our engagement with digital systems. As we increasingly interact with AI through conversation—whether by voice or text—we participate in the ongoing evolution of user interfaces. Embracing this shift can lead to more efficient, accessible, and personalized experiences in both personal and professional contexts.